Refrigeration is the process of generating a cooling effect by extracting heat from a lower temperature heat source and transferring it to a higher temperature heat sink, to maintain the temperature of the heat source below that of surroundings.
The domestic refrigerator found in our homes uses this principle to produce a cold temperature region in our refrigerator cabinets.
Heat transfer is the process by which heat travels from one point to another. Naturally, heat travels from a region of higher temperature to a lower temperature region. But refrigeration has made it possible to transfer heat from a low temperature source to a higher temperature sink, this is achieved by putting in work and the use of a working medium (refrigerant). The refrigerant absorbs the heat energy from a lower temperature reservoir and deposits the heat into a higher temperature reservoir by reason of the work done by a compressor (as in the case of the simple refrigerator).
Therefore, refrigeration can also be defined as the process of generating a cooling effect by extracting heat from a lower temperature heat source and transferring it to a higher temperature heat sink, to maintain the temperature of the heat source below that of surroundings by using a working medium (refrigerant). [1]
Refrigeration and air conditioning is a technology that has improved the quality of life of people every where in the world.
Refrigeration deals with cooling of bodies to temperatures lower than those of surroundings. This involves absorption of heat from a lower temperature isolated space and rejection of the heat to the higher temperature surroundings.
In the olden days, the primary objective of refrigeration was to create ice, which was used for preserving food, cooling drinks and to transport perishable goods etc.
Nowadays refrigeration and air conditioning are used in so many applications that they have become essential for life, and without refrigeration and air conditioning the ripple effects in all other industries will be immense.
Nevertheless, refrigeration is required for many applications other than air conditioning, and air conditioning also involves processes other than cooling and dehumidification.
Nowadays refrigeration has become an essential part of the food chain- from post-harvest heat removal to processing, distribution and storage. Refrigeration has become essential for many chemical and processing industries to improve the standard, quality, precision and efficiency of many manufacturing processes. Ever-new applications of refrigeration arise all the time. Some special applications require small capacities but are technically intriguing and challenging.
Air-conditioning is one of the major applications of refrigeration. Air-conditioning has made the living conditions more comfortable and healthy in workplaces and homes. Air conditioning involves control of temperature, humidity, cleanliness and circulation of air and air pressure to provide comfortable indoor conditions for human beings and/or some industrial requirements. Air-conditioning involves cooling and dehumidification in the summer months; this is essentially done by refrigeration. It also involves heating and humidification in cold climates, which is conventionally done by a boiler unless a heat pump is used.
Food processing, preservation and distribution:
Storage of perishable goods such as fruits and vegetables is very important in reducing spoilage and improving their shelf life.
Chemical and process industries:
Refrigeration is applied in chemical process, preservation and reactivity. Industrial processes such as LNG liquefaction, machine operations need refrigeration and air conditioning. Some machines which work at high temperature need to be regulated to a suitable operational temperature. Transportation of drugs and LPG also requires refrigeration to maintain their optimal condition.
Special applications of refrigeration:
In this set of applications, we consider applications other than chemical uses. These are in manufacturing processes, applications in medicine, construction units etc. these applications include; production of ice for sports activities, desalination of water, cold treatment of metals and medical application such as manufacturing of blood plasma and antibiotics.
Comfort air-conditioning:
Comfort air-conditioning aims to provide a conducive or comfortable atmosphere for human beings. Considering the suitable humidity, air flow, temperature, air pressure etc. that is needed for human comfort need to be controlled. This is the kind of air-conditioning that is found in our homes and offices. [2]
In the past years, diverse methods of achieving cooling have been developed. There are different methods of producing refrigeration, which include evaporative cooling, thermoelectric refrigeration, Ranque tube method of refrigeration, expandable refrigeration, Vapor compression refrigeration and Vapor Absorption refrigeration among others. [3]
Evaporative cooling refrigeration
Evaporative cooling uses the principle that cooling is achieved when a liquid absorbs heat equal to its latent heat of vaporization from the atmosphere as it evaporates.
For example, water being stored in a pitcher undergoes evaporative cooling. The water coming from the pores of the pitcher evaporates as it comes into contact with dry air, cooling the water in the earthen pitcher.
When a drop of spirit is placed on the palm, the cooling effect is caused by evaporation (evaporative cooling).
The cooling by evaporation can be described as the adiabatic heat transfer from air to water. It is used in cooling towers where water from the condenser is cooled by spraying it from the top and forcing an air current from below. Evaporative condenser types, desert coolers and room coolers are another application of evaporative cooling. These coolers pass dry air via wet sheets. The air is refrigerated because of evaporation. In the making of artificial snow, the theory is often used.
Thermoelectric refrigeration
When two dissimilar metals are joined together at two separate junctions, and connected to a power source. One end of the junction becomes colder while the other heats up. This principle is known as the Peltier effect of generating refrigeration. In contrast, when the junctions of the metals are kept at different temperatures, EMF is generated across the conductors .
Expandable refrigeration
The expandable refrigeration method is usually used for preservation of perishable goods especially in their transportation. It uses refrigerants that do not have negative effects on the goods such as Carbon dioxide (CO2), liquid helium and liquid nitrogen. The two types of expandable refrigeration are the evaporator system, where the refrigerant vaporizes in the evaporator. The refrigerant does not come into contact with the goods and the spray system, the refrigerant is sprayed directly on the goods [3].
Ranque tube method of refrigeration
Also known as the vortex tube, is a device with no moving parts which separates compressed air into hot and cold streams for refrigeration.
Compressed air is injected tangentially into a cylindrical chamber/vortex tube and rotates at high velocity.
The hot gas is separated from the cold due to differences in density and the effect of centrifugal force, as the denser gas (colder gas) swirls in the innermost section of the gas pushing the less dense (hot gas) to the outermost section. Due to the conical nozzle at the end of the tube, only the outer shell of the compressed gas is allowed to escape at that end as hot air. The remainder of the gas is forced to return in an inner vortex of reduced diameter within the outer vortex as cold air. Fig.4. below is a diagram of the Ranque tube or Vortex tube [4].
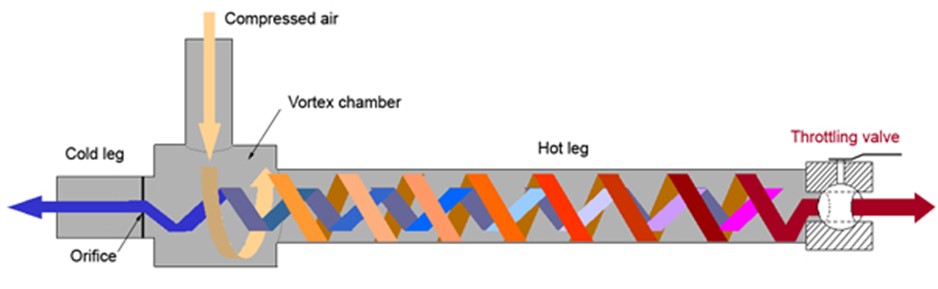 The Ranque Vortex Tube
The Ranque Vortex Tube
The Vapor Compression Refrigeration System
The ideal VCR system comprises four basic components namely, the evaporator, the compressor, the condenser and the expansion or throttling valve.
It is the most widely used refrigeration system in the world. The refrigerant enters the evaporator (located in the refrigerated space) as a low-pressure low temperature liquid refrigerant. Heat is transferred from the refrigerated space to the refrigerant in the evaporator. It is then sucked into the compressor as a saturated vapor where it is compressed to a high-pressure high temperature state and discharged to the condenser.
It is cooled to the saturated liquid state in the condenser. The liquid refrigerant is then throttled by the expansion valve to the evaporator pressure and vaporizes as it absorbs heat from the refrigerated space and produces the refrigeration effect as shown below.
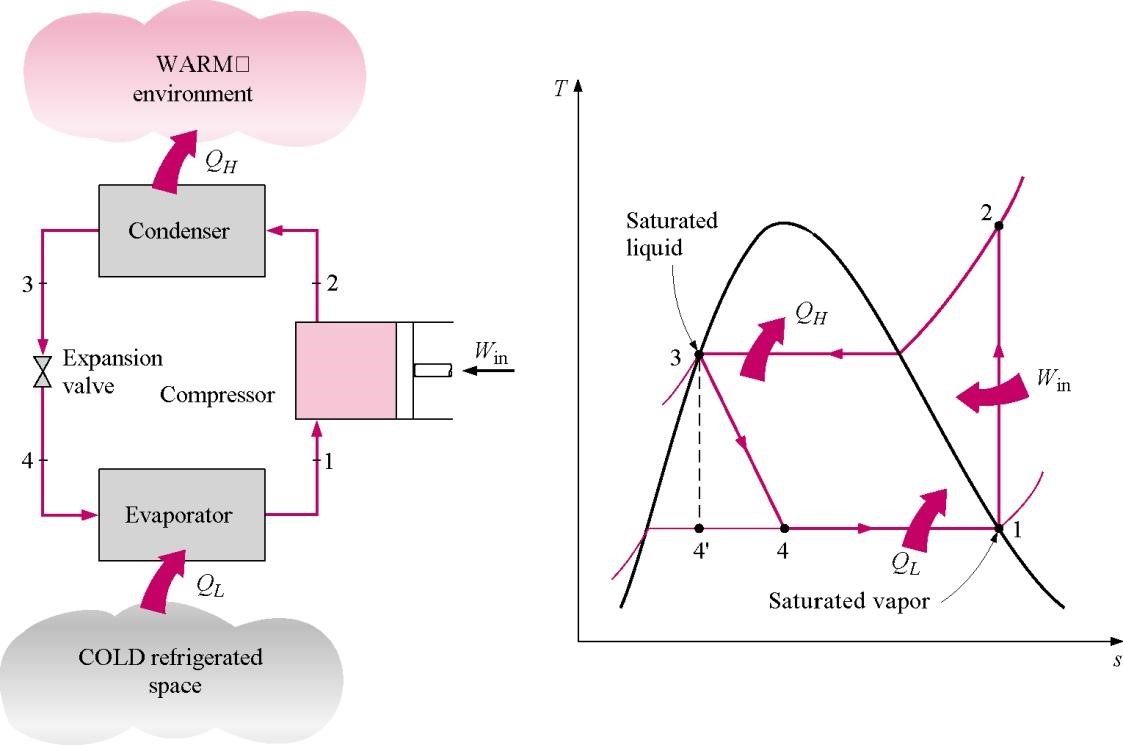 The Vapor Compression Refrigeration System
The Vapor Compression Refrigeration System
The Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System
The is just like the VCRs except that the compressor has been replaced by a complex absorption mechanism consisting of an absorber, a pump, a generator, a regenerator, a valve, and a rectifier.
The vaporized refrigerant leaves the evaporator and enters the absorber at low-pressure, where it dissolves and reacts with the absorbent to form a solution. Heat is released during this process, making it an exothermic reaction. The amount of refrigerant that can be dissolved in the absorbent is inversely proportional to the temperature.